Critical Role of Medical Specimen Transport in Modern Healthcare

In today’s complex healthcare landscape, medical specimen transport plays an essential yet often overlooked role in clinical diagnostics, patient management, and public health. The safe and timely delivery of biological specimens, such as blood, tissue, and microbiological samples, is fundamental to accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Advancements in transport protocols, technology, and regulatory standards have enhanced reliability and efficiency, contributing to improved patient outcomes and operational excellence in healthcare systems.

The Growing Importance of Medical Specimen Transport
Modern medicine relies heavily on laboratory testing for decision-making. Nearly 70% of clinical decisions are influenced by diagnostic test results. With the rise of specialized tests, rapid pathogen identification, and personalized medicine, the need for robust specimen transport systems has never been greater. Mismanagement or delays in specimen transport can compromise test results, leading to diagnostic errors, delayed treatments, and increased healthcare costs.
Key factors driving this growing significance include:
- Precision Medicine: Accurate genetic and molecular testing requires the integrity of transported specimens.
- Epidemiological Surveillance: Quick sample transport is crucial in managing outbreaks and emerging infectious diseases.
- Chronic Disease Management: Regular testing for chronic conditions demands seamless logistics to maintain care continuity.
Technical Aspects of Medical Specimen Transport
The transport of biological specimens is a highly regulated and technically complex process. Every stage—from collection to delivery—requires adherence to strict protocols to preserve specimen integrity and ensure patient safety. Below are critical technical considerations:
1. Preservation and Stability
Specimen degradation is a major concern. Different types of samples have specific temperature and handling requirements:
- Ambient transport: Suitable for routine blood tests and swabs.
- Refrigerated transport (2–8°C): Necessary for chemistry panels, coagulation studies, and certain microbiological specimens.
- Frozen transport (-20°C or below): Essential for molecular assays and long-term specimen storage.
Failure to maintain appropriate conditions may render the specimen unusable, compromising diagnostic accuracy.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Strict guidelines govern the transport of medical specimens to minimize risks to public health and ensure the safety of transport personnel. International standards, such as those from the International Air Transport Association (IATA) for air transport, and local regulations, like OSHA’s bloodborne pathogen standards, dictate packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements.
Key regulatory elements include:
- Triple-layered packaging systems to prevent leaks and contamination.
- Proper classification of specimens as Category A or B infectious substances.
- Accurate documentation for traceability and compliance audits.
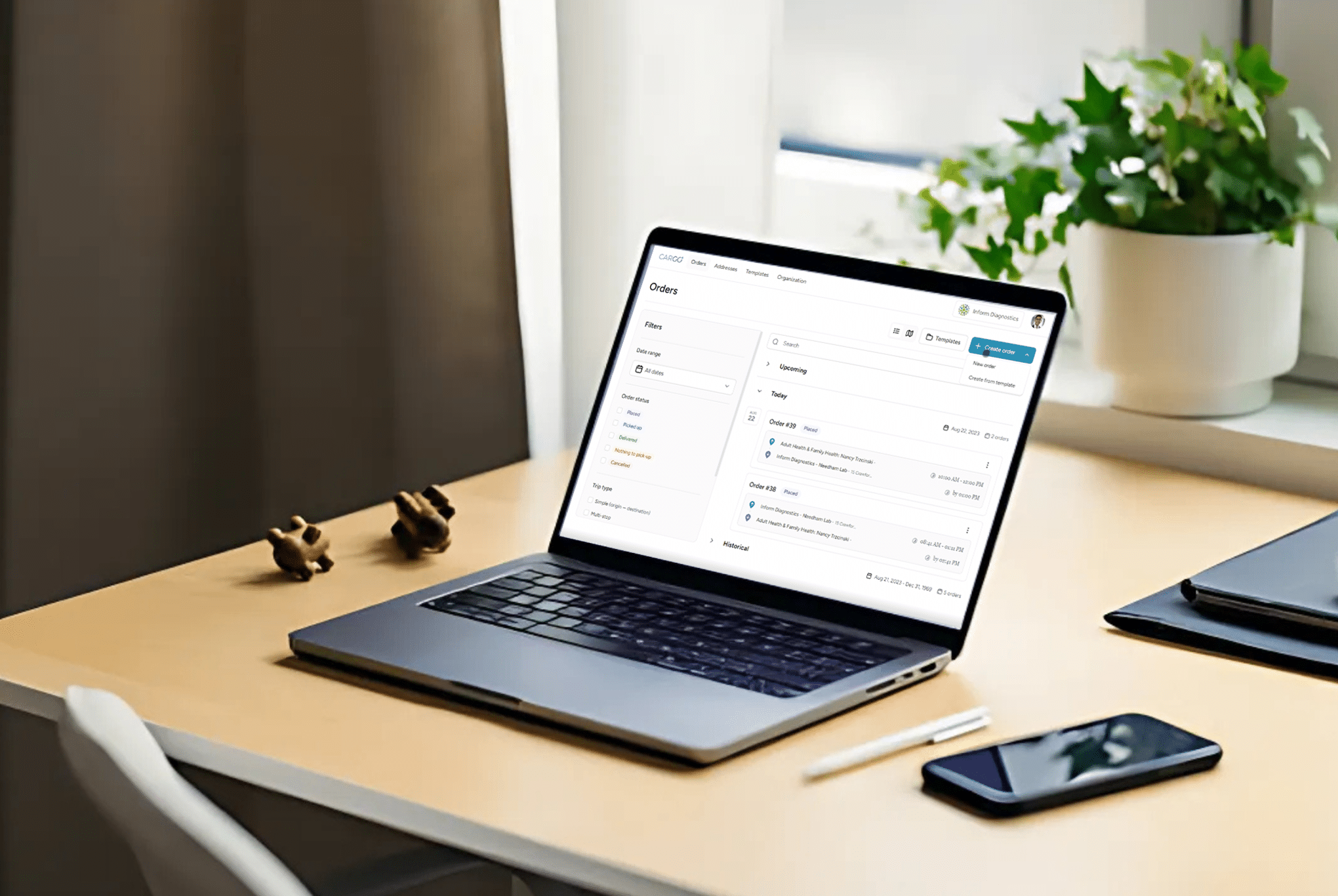
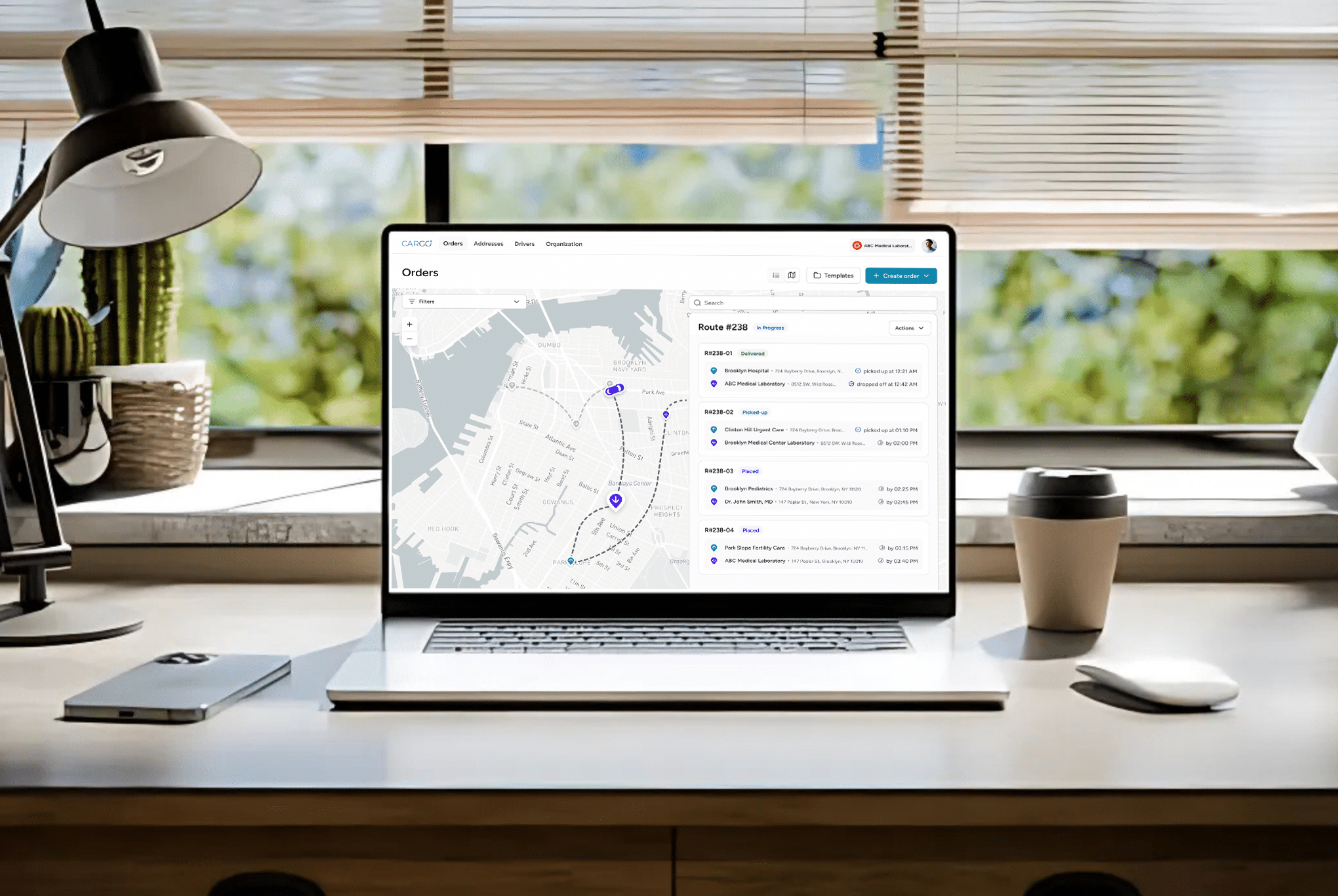
3. Chain of Custody and Real-Time Tracking
Maintaining a verifiable chain of custody is critical for legal and clinical accuracy. Modern transport systems utilize advanced tracking technologies, including GPS and RFID, to monitor specimen location, temperature, and handling conditions in real-time. These systems ensure transparency and enhance accountability, reducing the likelihood of errors.
Technology Driving Innovation in Specimen Logistics
Technological advances are reshaping the field of medical specimen transport, focusing on improved efficiency, data integration, and automation. Emerging innovations include:
- Temperature-controlled smart containers with real-time monitoring.
- Automated dispatch and routing algorithms for optimized logistics.
- Drone technology for rapid delivery in remote or inaccessible regions.
Additionally, integrating transport data into laboratory information systems (LIS) provides healthcare providers with real-time visibility into specimen status, enabling better clinical decision-making.
Operational Challenges and Solutions
Despite technological progress, specimen transport faces ongoing challenges that require strategic solutions:
1. Geographic and Logistical Barriers
In rural or underserved areas, accessing laboratory facilities may be difficult. Solutions include regional transport hubs, mobile laboratories, and strategic partnerships with third-party logistics providers.
2. Specimen Handling Errors
Human error remains a persistent risk, especially during collection, labeling, and transfer. Automation and continuous staff training help mitigate these risks.
3. Regulatory Complexity
Navigating the diverse regulatory landscape can be challenging for global operations. Standardizing protocols and maintaining comprehensive compliance management systems can streamline processes.
The Future of Medical Specimen Transport
The future of medical specimen transport will be driven by increased digitization, enhanced data integration, and further automation. As healthcare becomes more personalized and data-driven, reliable specimen transport systems will remain a cornerstone of quality care. Collaboration across clinical, regulatory, and technological domains will be essential to address emerging challenges and seize new opportunities.
In an era of precision medicine and rapid diagnostics, efficient and reliable specimen transport is not merely a logistical necessity but a vital component of modern healthcare. Its continued evolution will support the delivery of faster, more accurate, and patient-centered care.